
A-Level数学相较于高考数学难度更大,而且涉及到很多大学才需要学习的知识点,比如微积分、二项式等,今天,跟随锦秋狄欣萍来了解一下二项式分布模型的相关知识点。
二项分布是离散的概率分布,它描述了一个实验中n个独立试验的结果。每个试验都假定只有两种结果,要么成功,要么失败。如果一次试验成功的概率是p,那么事件X,即在n次独立试验中k次试验成功的概率为:
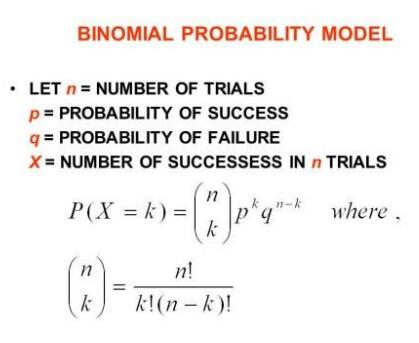
当然,二项式模型的运用是有前提条件的,在Alevel中,我们被要求掌握四种:
1. 在每次试验中只有两种可能的结果
2. 每次实验是互相独立的
3. 成功事件的概率为固定值
4. 总实验次数为固定值
我们来看一道比较简单且经典的二项式分布题型:
Suppose there are twelve multiple choice questions in an English class quiz. Each question has five possible answers, and only one of them is correct. Find the probability of having four or less correct answers if a student attempts to answer every question at random.
我们来分析下解题思路:
Since only one out of five possible answers is correct, the probability of answering a question correctly by random is 1/5=0.2. We can find the probability of having exactly 4 correct answers by random attempts as follows.
We define X as the number of correct questions we answered
P(X=4)=12C4*0.2^4*0.8^8
出于过程简洁度考虑,之后笔者用R语言来计算:
> dbinom(4, size=12, prob=0.2)
[1] 0.1329
To find the probability of having four or less correct answers by random attempts, we apply the function dbinom with x = 0,…,4.
> dbinom(0, size=12, prob=0.2) +
+ dbinom(1, size=12, prob=0.2) +
+ dbinom(2, size=12, prob=0.2) +
+ dbinom(3, size=12, prob=0.2) +
+ dbinom(4, size=12, prob=0.2)
[1] 0.9274
当然Alevel的同学可以直接通过书后的cumulative probability表来查询连续性概率;AP的同学可直接通过计算器计算得出:
> pbinom(4, size=12, prob=0.2)
[1] 0.92744
在考试中,我们需要注意分析总实验次数,成功事件的概率以及考虑到成功事件发生的次数,比如 at least 是大于等于,more than是大于,作为离散变量模型,一定要注意是否有等号。
更多有关A-Level科目及考试等方面的信息,大家可以扫码关注锦秋A-Level进行了解,锦秋A-Level紧抓中国学生理科优势,进行课程组合化。开设数学、物理、化学、生物、经济学、会计学等课程,帮助学生以优异成绩申请更好的大学。

| 大学名称 | QS排名 |
|---|