
锦秋A-Level学院作为隶属于新航道国际教育集团的高端子品牌,专为有志于申请英国G5及英澳高校的中学生设计,紧抓中国学生理科优势,进行课程组合化。开设数学、物理、化学、生物、经济学、会计学等课程,帮助学生以优异成绩申请更好的大学。
今天为大家分享的是A-Level化学的备考讲解,为大家重点讲解关于烷烃类(ALKANEs)物质性质的内容。希望能够给A-Level化学迷茫的同学指点迷津。
物理性质
1. 物质状态:
At room temperature and pressure:
• C1 - C4 are gases
• C5 - C15 are liquids
• C16 - are solids.
2. 沸点性质变化规律:
(1)烃类物质,随着物质分子质量越大,其沸点越高。As the number of carbon atoms in a straight chain alkane increases, the boiling points rise in a uniform and predictable manner.
This is because each molecule is identical in terms of types of atom and bonds present, the only difference being the regular increase in mass.
(2)质量相近,物质分支越多,沸点越低。Compounds with branched chains always have boiling points below that of the related straight chain compound.
比如:
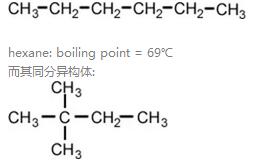
2,2-dimethylbutane的沸点boiling point = 49℃.
现象解释:支链越多,分子间作用力越小。This is because the straight chain molecules have greater areas of contact between them and hence have stronger forces of attraction.
3. 熔点性质变化规律:
(1) 分子质量越大,熔点越高。The melting point also increases with the number of carbon atoms in the chain.
(2) 奇数个碳原子构成的烃类物质分子间作用力小,偶数个碳原子构成的烃类物质分子间作用力大。因此熔点比较要区分分子个数的奇偶性。However, when plotted on a graph, two curves are obtained due to the fact that 'even' carbon molecules pack tighter together, and therefore van der Waal's forces are greater than 'odd' carbon molecules.
4. 溶解性:
烃类物质是非极性分子,因此不易溶于水溶液。在烃类物质中,甲烷在水中的溶解性最强。The alkanes are non-polar and are therefore immiscible in water and other polar solvents. Methane is the most soluble.
化学性质
烃类化合物大多是非极性分子,化学反应活性不大,相对来说比较稳定。总体来说。The C-C and C-H bonds in alkanes are very strong since they are non-polar and almost totally covalent in character. Therefore, alkanes are relatively inert with regard to most chemical reagents.
主要有三类反应,具体如下:
1. Combustion燃烧
2. Substitution reactions取代反应
3. Catalytic (or thermal cracking)催化反应
1. 燃烧反应Combustion
The alkanes burn in a plentiful supply of oxygen to produce CO2 and H2O.烃类物质与氧气反应可生成二氧化碳和水。
比如:
2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
方程式要记得配平哦~
烃类气体和氧气的混合物易燃易爆,要小心使用。A gaseous mixture of an alkane and oxygen are extremely explosive. These reactions are used commercially when fuels such as natural gas, petrol and oil are burnt in air.
2.取代反应,尤其是甲烷的取代反应是学习重点。
Substitution reactions involving chlorine and methane
(1) 混合甲烷和氯气后,如给予光照或者是紫外线,可发生取代反应。
具体的反应条件描述如下:
A mixture of chlorine and methane:
• a) Does not react if kept in the dark at room temp.
• b) Does not react if kept in the dark at 300oC
• c) Reacts at room temperature if exposed to sunlight or U.V. light.
• d) Explodes if exposed to bright sunlight or sparked.
也就是说,氯取代甲烷的反应是吸热反应。So, energy is required to initiate the reaction.
Four products are formed from this reaction:
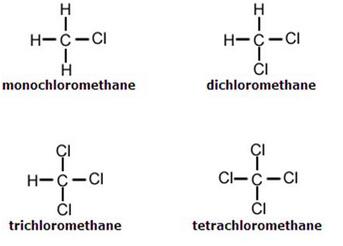
(2) 反应方程式如下: These products are explained in terms of a stepwise reaction:
• CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g)
• CH3Cl(g) + Cl2(g) → CH2Cl2(g) + HCl(g)
• CH2Cl2(g) + Cl2(g) → CHCl3(g) + HCl(g)
• CHCl3(g) + Cl2(g) → CCl4(g) + HCl(g)
Each of these reactions is an example of a substitution reaction (a Cl atom is substituted for a H atom).
(3) 反应机理Mechanism: 自由基取代Free radical substitution
It has been shown that the reaction will proceed in the presence of a free radical.自由基取代反应是指自由基试剂与底物发生的取代反应。
反应过程分为三步:
a) 引发反应 Initiation:光或热引发自由基的生成。Light or heat will cause a few chlorine molecules to split homolytically into chlorine radicals having unpaired electrons. 成键的一对电子平均分给两个原子或集团,这种断裂方式为均裂( hemolytic)。均裂时生成的原子或基团带有一个孤单电子,用黑点表示。带有孤电子的原子或原子团称为自由基(free radical)。自由基是中性的,大多数只有瞬间寿命,是活性中间体的一种。
反应为:Cl:Cl(g) → 2Clo(g) (chlorine radical)
b) 增长反应Propagation:
自由基与反应粒子结合。The radicals are very reactive and will react with the first particle they meet - most probably a methane molecule because the formation of a H-Cl bond is more exothermic than the formation of a C-Cl bond.
• i) Clo(g) + CH4(g) → oCH3(g) + HCl(g)
(formation of a methyl radical is more likely)
Or:
• Clo(g) + CH4(g) → CH3Cl(g) + Ho(g)
The methyl radical produced initiates further propagation steps:
• ii) oCH3(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) + Clo(g)
• iii) CH3Cl(g) + Clo(g) → oCH2Cl(g) + HCl(g)
• iv) oCH2Cl(g) + Cl2(g) → CH2Cl2(g) + Clo(g)
• v) CH2Cl2(g) + Clo(g) → oCHCl2(g) + HCl(g)
c) 反应终止Termination:
当没有新的自由基产生的时候,反应终止。Some reactions occur in which atoms or radicals combine together to produce a molecule without a new radical being formed:
• Clo(g) + Clo(g) → Cl2(g)
•oCH3(g) + Clo(g) → CH3Cl(g)
•oCH2Cl(g) + Clo(g) → CH2Cl2(g)
Radicals are removed from the system thus preventing the chain reaction going to completion.
类似于氯代反应,溴代反应也可发生,但是需要更多的能量,碘代反应不发生。 Bromination of methane occurs by a similar mechanism but requires more energy. Iodination does not take place.
热裂解可把大分子烃类分解为碳个数较少的小分子物质。由于碳断裂位置不固定,产物多为多种产品的混合物。Thermo-crackingis used to break down high molecular mass alkanes into low molecular mass alkanes as well as alkenes using heat and a catalyst. As bond breaking is a random process, a variety of products can be formed.
For example:
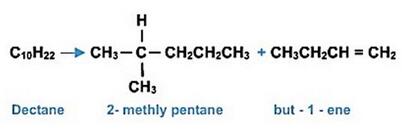
锦秋A-Level学院拥有完备的学员服务系统,专业的师资团队、服务团队、留学团队为学生G5申请环环把关,一路保驾护航。总而言之,一切都是有可能的,没有什么是遥不可及的,专业申请策略加上个人的努力,英国G5不是梦!
| 大学名称 | QS排名 |
|---|---|
| 麻省理工学院 | 1 |
| 剑桥大学 | 3 |
| 斯坦福大学 | 3 |
| 牛津大学 | 2 |
| 哈佛大学 | 5 |
| 加州理工学院 | 6 |
| 帝国理工学院 | 7 |
| 伦敦大学学院 | 8 |
| 苏黎世联邦理工大学 | 8 |
| 芝加哥大学 | 10 |
| 新加坡国立大学 | 11 |
| 宾夕法尼亚大学 | 13 |
| 洛桑联邦理工学院 | 14 |
网络优惠
预约试听
A-Level
雅思
留学咨询
留学规划