
化学通常被认为是最难的A-Level课程之一,不仅是因为内容难度大,还需要学生把化学知识联系到各种实际情况中。接下来,跟着锦秋化学组老师回顾一下10月的A-Level化学U2—U3的考情,整理出2021年1月的备考方向。
2020年10月A-Level化学U2考情分析
考试代码及时间:
WCH12/01,2020年10月9日
01.C。
考察物质enthalpy change of atomisation 和bond energy的定义,尤其需要注意定义中初始状态和结束状态以及单位摩尔所带来的正负号和倍数关系。
E(Cl-Cl) 为1 mol Cl-Cl被打破,从1mol Cl₂(g)生成 2 mol Cl(g), enthalpy change of Cl为 1/2 mol Cl₂(g) 生成 1 mol Cl(g)。所以两个过程正负号相同但enthalpy change of Cl 是已知量的 1/2。
02.A。
考察enthalpy change的正负号对应吸热还是放热,温度升高还是降低。
03.D。
考察水和冰里H键特性,D为ion-dipole interaction。
04.D。
考察有机物中决定boiling point的因素,题中是同一种homologous所以分子间作用力类型相同,并且同样数量的C的,所以C链结构决定boiling point,branch越多,接触点越少,分子间作用力越少,boiling point越低。
05.
a) B。考察基础反应类型,H₂O₂里的O化合价同时升高和降低。
b) B。考察stoichiometry,molar volume相关计算,注意单位转化和对应的物质。nH₂O₂: no₂ =2:1, no₂= Vo₂/ Vm
06.A。
考察通过元素电荷守恒配平方程,并不需要使用Cr的化合价变化情况。左边7个O所以z为7,x为14,y为6。
07.D。
考察化合物中所有元素化合价相加为0,以及化合价和角标的关系,K为group I,所以化合价为+1。
08.a) B。考察flame test金属和对应颜色,以及nitrate热分解规律。red可能是Li⁺/ Ca²⁺/ Sr²⁺,Li和group II所有金属的nitrate都可以热分解出NO₂。
b) A。考察NO₂的无机鉴定,红棕色酸性气体,使litmus变红。
09.A。
考察F⁻的和浓硫酸的氧化还原反应,以及X⁻的还原性变化规律,F⁻还原性不会和浓硫酸发生redox。
10.a) B。考察enthalpy profile中enthalpy change定义(反应物指向生成物)。
b) C。考察activation energy定义(反应物指向能量点),注意题目问的是逆过程,反应物为P
c) C。考察Hess’s law在profile的应用,箭头向上为正值,向下为负值。v+x = 0, A错;w-x = u,B错;u-v = w,D错。
11.a) B。考察stoichiometry,molar volume,molar mass,limiting reagent相关计算。8.43g MgCO₃,为0.1mol,nMgCO₃: nHCl =1:2, 所以HCl 为limiting reagent,nCO₂: nHCl =1:2,生成 0.05mol CO2,VCO₂= nCO₂ x Vmo
b) B。考察反应速率,生成物V-t图,上升但斜率下降。
c) A。考察反应速率,rate-t图,随着反应进行,反应物浓度降低所以反应速率会降低,只有A符合该特征。
12.a) D。考察有机物命名,E/ Z判断标准,functional group的locant选取标准。C=C两端priority高的group在异侧为E,以-OH所在位为基准,C=C在5号位。
b) A。考察C=C加成反应。
c) C。考察R-OH制备R-Cl的reagent,需要注意该reagent不能与C=C发生反应。
13.a)
ⅰ) 考察Hess’s cycle及元素配平,因为下方为oxides,所以由enthalpy change of combustion推 enthalpy change of reaction,
• 箭头向下指向oxides,生成 3CO2 + 4H2O。
ⅱ) Hess’s cycle需要enthalpy change of combustion,但题目提供的是enthalpy change of combustion,考察氧化物生成晗和对应单质燃烧晗的关系,H2O的生成晗可直接替代H2的燃烧晗,CO2的生成晗可直接替代C的燃烧晗。
• △H= 3x(-393)+4x(-285.8)-(-2219) = -103.2kJ mol-1
b)
ⅰ) 找alkane结构上的规律
• chain increase by 1 -CH2 unit,
• each -CH2 release same amount of energy。
ⅱ) 链接alkane的physical state和enthalpy change,因为燃烧时液体会发生气化,所以燃烧焓会受到影响。
• pentane is a liquid, so energy is needed to turn it into gas,
• therefore increase in enthalpy change of combustion of from butane to pentane is less.
ⅲ) 考察分子间作用力之London force及其影响因素
• alkanes are non-polar, only have London force;
• London force increases as total number of electrons increases;
so during the boiling process, more energy is needed to overcome the intermolecular force.
14.a) 考察CO2和Ca(OH)2的基础反应,状态符号占分
• CO2(g)+Ca(OH)2(aq) —> CaCO3(s)+H2O(l)
b) 考察酸碱滴定计算
• nHCl =0.05x 23.4x10-3 = 1.17x10-3 mol
• nCa(OH)₂ : nHCl = 1:2
nCa(OH)₂ = 5.85x10-4 mol
• mCa(OH)₂ = 5.85x10-4 x74.1 = 0.0433 g
• [Ca(OH)₂] = m/V = 0.0433/ 25x10-3 = 1.73 g dm-3
c) 考察group II hydroxide 溶解度变化趋势
• Mg(OH)2 is less soluble than Ca(OH)2,
so less amount of Mg(OH)2 in the solution, less acid is needed to get it neutralised, hence smaller titre.
15.
a) 考察通过化合价判断redox
• Ag: 0 —> +1 increase in o.s. Ag is oxidised
• N: +5 —> +4 decrees in o.s. HNO3 is reduced
b)
i) 考察通过实验方式求enthalpy change,Q= mc△T , △H= -Q/n, c= n/V, 需要额外注意kJ到J,cm3到dm3的单位转化。
c= -mc△T/△H/V = -(50x4.18x5.2)/(36.1x103)/ (50x10-3) = 0.602 mol dm-3
ⅱ)考察stoichiometry, molar mass, concentration相关计算
c=n/V=m/M/V= 5.96/(107.9+79.9)/ (50x10-3) = 0.635 mol dm-3
ⅲ) 考察enthalpy change 和precipitation实验的误差分析
• A: heat loss, Q recorded is less than actual value
• B: solid produced is not dried, mass of solid is larger than actual value
16.a) 考察基础有机反应试剂,条件和反应类型
b)
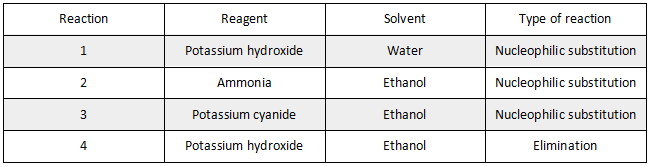
c) Butanenitrile
d) 考察nucleophilic substitution反应机理,
• 需要标注反应物中的partial charge,C偏正Br偏负;
• curly arrow 箭头由NH3的lone pair指向 C;
• 最后一步deprotonation,curly arrow箭头由Br-的lone pair指向 NH4+里的H;画出正确的产物
e) 考察halogenoalkane 水解影响反应速率的因素, 1) C-Cl, C-Br, C-I键的强度及解释;2) primary, secondary, tertiary halogenoalkane水解生成的C+intermediate的稳定性及解释。注意6分题中6个题目要点都答到得4分,另2分为答题逻辑。
• Hydrolysis is nucleophilic substitution
• The easier C-X breaks, the shorter time taken for ppt to appear
• Compare experiment 2,1 and 3, rate gets faster because bond strength decrease from C-Cl to C-Br to C-I
• Since size of halogen atoms getting larger
• Compare experiment 4, 2 and 5, rate gets faster because intermediate C+ is primary, secondary and tertiary respectively, which gets more stable
• Since the more alkyl groups attached, the more electrons could be donated to stablise the C+.
17.a)
ⅰ) 考察压强对反应速率和反应平衡的影响
• High pressure increases reaction rate
• and yield since reaction favors lower pressure side which is product side as there are less number of gas molecules.
ⅱ) 考察温度对反应速率和反应平衡的影响
• High temperature increases reaction rate
• but lower the yield since the reaction favors low temperature side, as the reaction is exothermic, equilibrium will shift to reactant side.
• So a compromising T of 250oC is chosen.
ⅲ) 考察催化剂基础定义
• Catalyst remains unchanged after reaction, so can be reused.
b)
ⅰ) 考察alcohol的氧化反应
• Acidified K2Cr2O7
• Heat under reflux
ⅱ) 考察氧化反应的配平
CH3OH + 2 [O]—> HCOOH + H2O
ⅲ) 考察carboxylic鉴定
• Mg ribbon
• Bubble
ⅳ) 考察IR图谱
• Methanol: O-H (alcohol) 3750-3200 cm-1; C-H (alkane) 2962-2853 cm-1
• Methanoic acid: O-H (carboxylic acid) 3300-2500 cm-1, C=O (carboxylic acid) 1725-1700 cm-1
• When all methanol has been converted to methanoic acid O-H (alcohol) 3750-3200 cm-1; C-H (alkane) 2962-2853 cm-1 disappears, O-H (carboxylic acid) 3300-2500 cm-1, C=O (carboxylic acid) 1725-1700 cm-1 can be seen
c) 考察Green chemistry
ⅰ)
• Methanol produced by CCU is a carbon neutral fuel
• But only 5% of methanol is used, so 95% of fuel still releases CO2 which would cause global temperature increase but to a less extent.
ⅱ) 考察octane的完全燃烧反应方程,
• nC⁸H¹⁸ : nCO2 = 1:8
• mCO2= n x M = 8 x 44= 452 g
ⅲ) 结合a) 里的方程,
• mCH3OH used = 1200kg x 5% = 60 kg
• nCH3OH= 60/ 32 = 1.875 kmol, n = 1.875 kmol
mCO2 = 1.875 x 44 = 82.5 kg

2020年10月A-Level化学U3考情分析
考试代码及时间:
WCH13/01,2020年10月14日
1.White anhydrous solid contain one cation and one anion. Heat in test tube to produce a brown gas; glowing splint relit; white solid remain.
传统无机分析题
(a) Brown gas: 棕色气体生成,只有一种可能,即NO2, nitrogen dioxide
Glowing splint relit: 带火星木条复燃,经典的氧气鉴别反应。即O2, oxygen。真题中对“复燃”的描述还有”relight”和”reignite”。
(b) 同时生成NO2与O2的反应只有硝酸盐nitrate NO3- 受热分解。除此之外爱德思版本考试中只会学到碳酸盐carbonate CO32-受热分解生成CO2。高锰酸盐Manganate MnO4-分解生成O2、氯酸盐chlorate(V) ClO3-分解生成O2、氢氧化物Hydroxide OH-分解生成H2O 的反应并不是新大纲要求。
(c) Flame test: green colour. 只能是Barium ion Ba2+。另外需要记住的还有:Li+ red; Na+ yellow; K+ lilac; Mg2+ colourless; Ca2+ orange(yellow-red); Sr2+ red。
(d) 总化学式:Ba(NO3)2,分解剩余固体BaO。注意此处要求只写formula。如果是NaNO3或KNO3分解后只能得到nitrite NaNO2和KNO2及氧气O2。
氢氧化物hydroxide和硫酸盐sulfate的溶解性题。此处加NaOH没有现象(缺乏化学驱动力chemical driving force),加入H2SO4则会生成BaSO4 white precipitate。
2.HCl, K2CO3, AgNO3, NaCl四种物质溶液相互混合。
新型无机分析题
(a) B+C→white ppt, not dissolve in H2SO4。说明此沉淀只能是AgCl,B和C应分别是AgNO3 和HCl或NaCl。
B+D→ppt, dissolve in HNO3。说明此沉淀只能是Ag2CO3。B与E应分别是AgNO3和K2CO3。与上条结合可见B是AgNO3,D是K2CO3。
B+E→white ppt, not dissolve in HNO3。同条,E应是HCl或NaCl。
C+D→colourless gas given off。只能是HCl+ K2CO3生成CO2。结合/第二条可得C为HCl。相应的E为NaCl。
(b) 焰色反应步骤题。
三个改进分别是:
①溶解样品应用concentrated HCl而不是HNO3,之前官方对此的解释是”evaporate when heated in Bunsen burner”,其实这与氯离子的配位作用也有关,再次不表。
②copper wire应换为platium (or nichrome) wire。因为铜本身会产生焰色而影响观测interference of copper flame colour。
③air hole close应open。Bunsen burner之所以火焰无色就是靠充分燃烧的高温need sufficient combustion。
3.F,G,H three organic liquid, each contain one functional group.
经典有机分析题
(a) (i) Test1: +PCl5→steamy fume, turn damp blue litmus paper red.
Steamy fume是HCl(g)的标志性现象,而溶于水后显酸性也验证了产物。说明F与G含有-OH。
(ii) Test2: +NaHCO3→G: gas given off, turn limewater cloudy.
Limewater(澄清)水灰水也是验证CO2气体的标志性反应,证明G是一个酸acid。
(iii) 此二实验说明F应该是alcohol,G是carboxylic acid。注意此处应该应该写官能团的名字而不是结构式。
(iv)F,G二者相对质量molar mass皆为46,根据官能团可得F为C2H5OH,G只可能是HCOOH。此处涉及到”organic family”或者说”homologous series”的知识,分子量较小也使得分子结构没有其他的可能。注意此处要求display formula。
(v)因为二者包含的化学键不同,IR图区分会非常明显。此类题目注意即使是同分异构体isomer,IR图中fingerprint area也会有所区别。
(b)根据题目对鉴别试验的描述也可以看出H中的官能团,即C=C会使bromine water褪色brown liquid goes colourless; -CHO会使Benedict’s/Fehling’s reagent产生brick red precipitate。
4.中和焓测定。标准物理化学题
(a)A,B二者的反应使其一A过量excess永远是为了让B完全反应completely reacted.
(b)读取温度计读数并计算ΔT。
(c)计算放热E进而计算ΔH=E/n。注意此处n应为生成H2O或者说反映的HCl的数量。
(d)用玻璃烧杯glass beaker的话相比于泡沫塑料(聚苯乙烯)杯polystyene cup肯定会造成更多的热损失heat loss,进而导致less exothermic enthalpy change。
5.滴定操作题
(a) 此处量度20cm3液体的仪器是一个固定答案:pipette and pipette filler。如果量度量更大的话则需measuring cylinder。
(b)判定指示剂颜色变化的题目重点是判断在滴定终点附近的酸碱度变化。以HCl为标准溶液滴定carbonate solution的话应是碱性变为中性,对于指示剂methyl orange来说应是yellow to orange。注意不要变为酸性条件下的red,变为酸性说明酸过量了。类似的还可能考到酚酞phenolphthalein和石蕊litmus的颜色变化。
(c) 取mean titre时的标准为选两个”concordant value”,即差值在0.2cm3内的数值,再做平均。从经验上来说一般个titre会作为rough titration。
因为此处M2CO3待测液有25cm3,所以如果是总量(250cm3)的话则需×10。
注意M2CO3将以1:2的比例与HCl反应,可以算出M的相对原子量23,为Na。
(a) 标准的”prepare salt form solution”的操作,即:
①evaporate until crystal appear
②filter to get crystal
③wash with cold solvent
④dry with filter paper
作为3分题第③点应该不算分。
更多A-Level科目考情分析及真题试卷信息,大家可以查看《锦秋2020年10月A-Level热门科目考情分析及1月备考指导》一文进行了解,或者扫码关注锦秋A-Level进行了解,锦秋A-Level设置一站式计划、学霸计划、国际班互补计划三大课程体系,开设数学、进阶数学、物理、化学、生物、经济学、会计学等优势学科,一对一规划学习方案,满足学生不同层次的学习需求。

| 大学名称 | QS排名 |
|---|---|
| 麻省理工学院 | 1 |
| 剑桥大学 | 3 |
| 斯坦福大学 | 3 |
| 牛津大学 | 2 |
| 哈佛大学 | 5 |
| 加州理工学院 | 6 |
| 帝国理工学院 | 7 |
| 伦敦大学学院 | 8 |
| 苏黎世联邦理工大学 | 8 |
| 芝加哥大学 | 10 |
| 新加坡国立大学 | 11 |
| 宾夕法尼亚大学 | 13 |
| 洛桑联邦理工学院 | 14 |
网络优惠
预约试听
A-Level
雅思
留学咨询
留学规划